Mostly Physics Simulations
Wave Equation
Ising Model
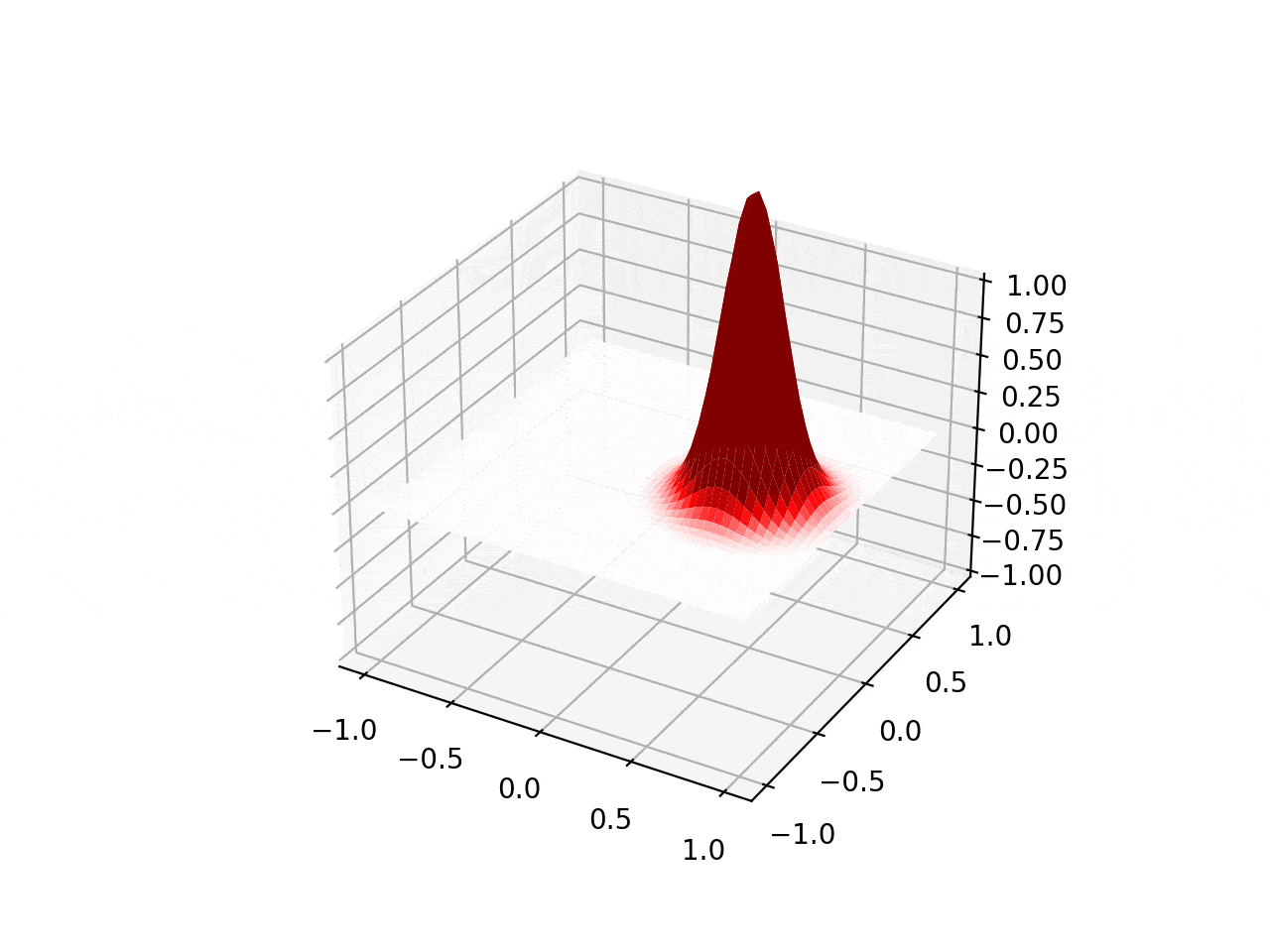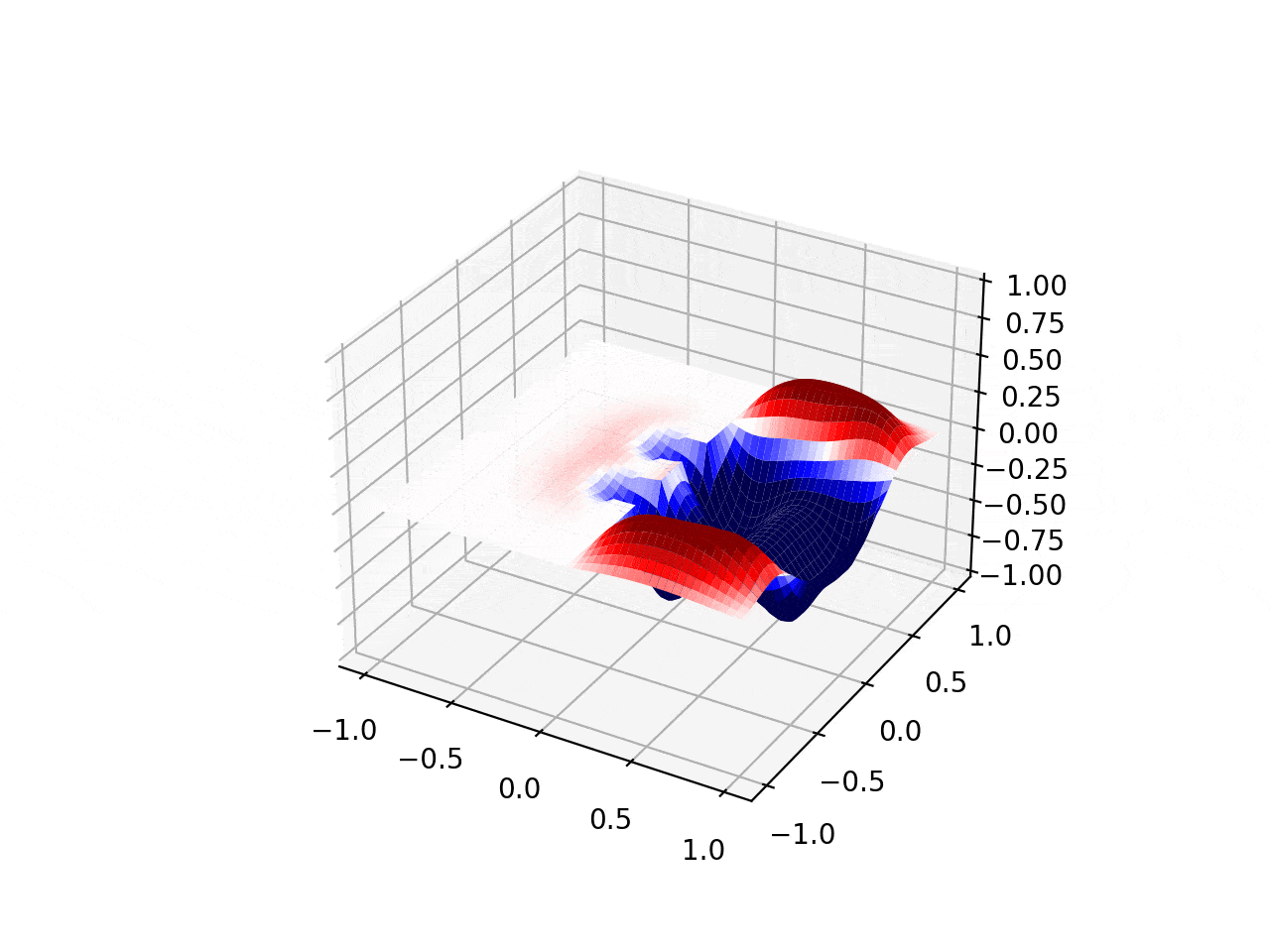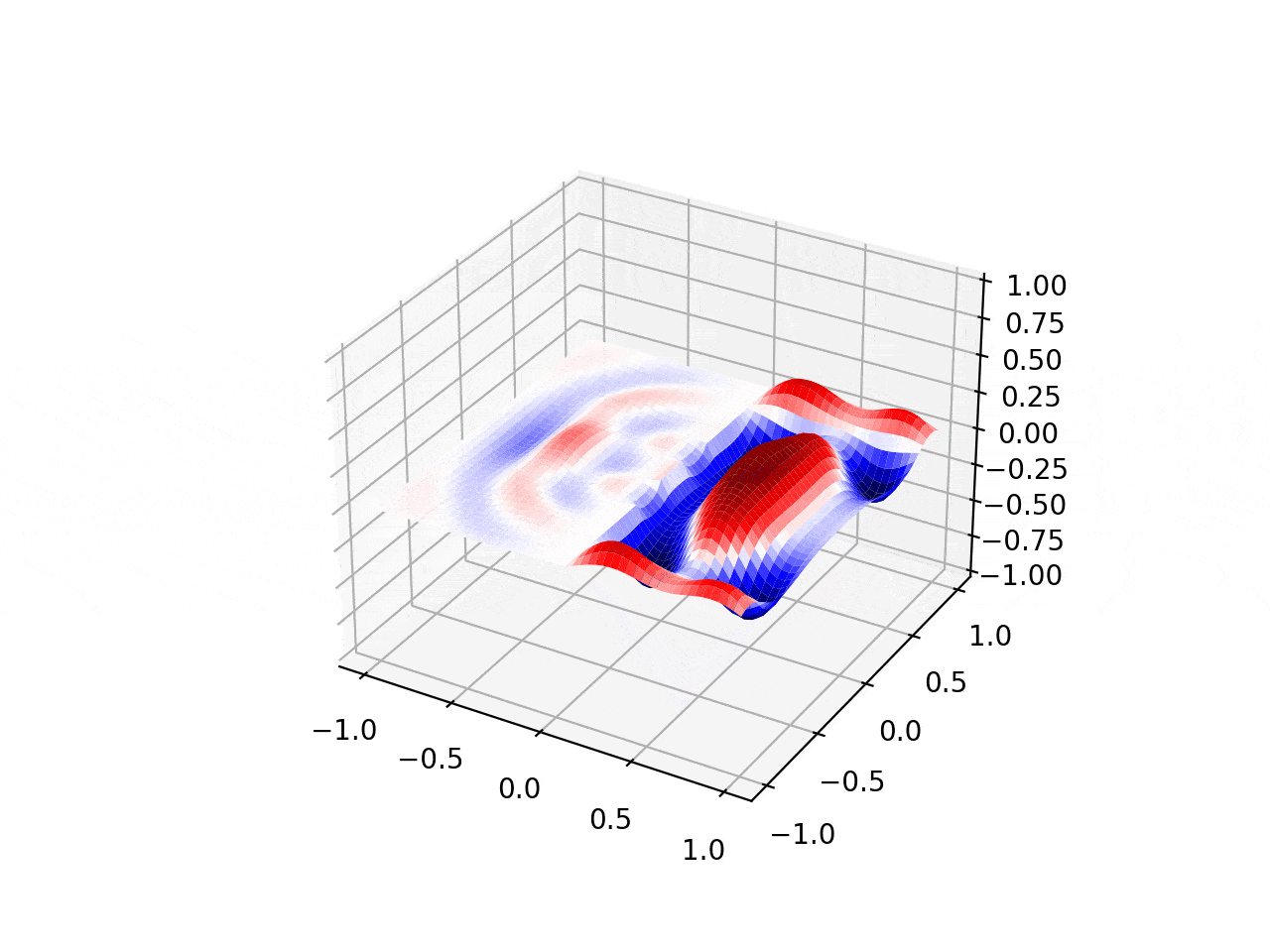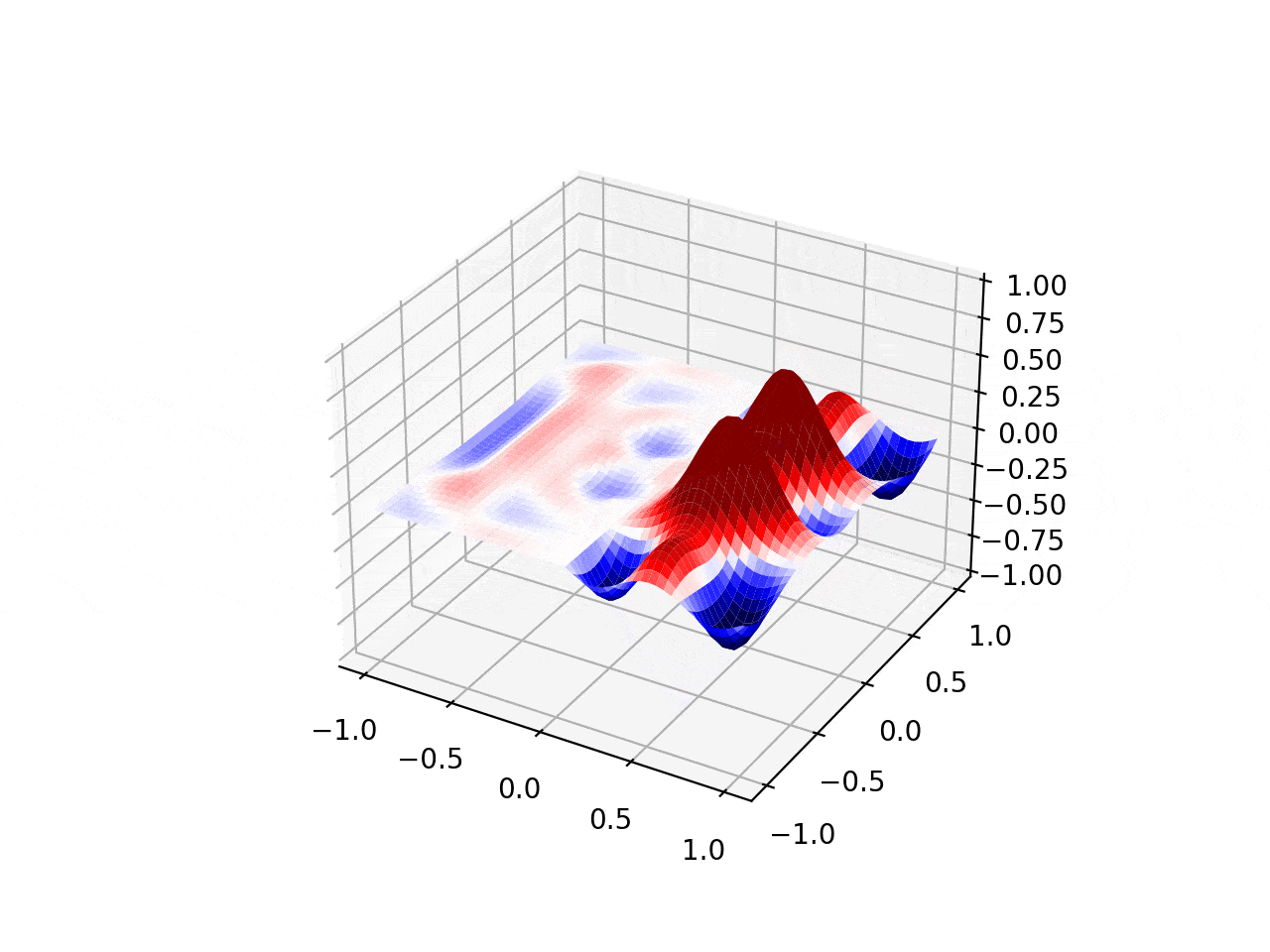
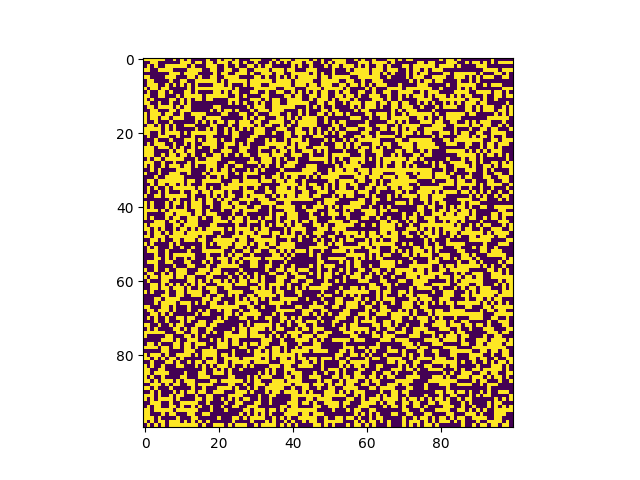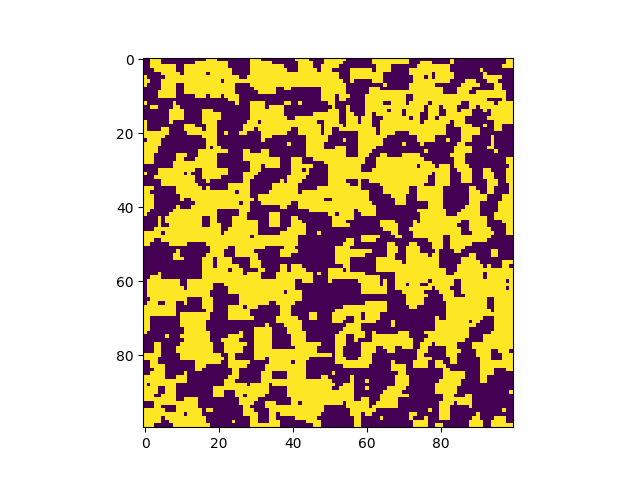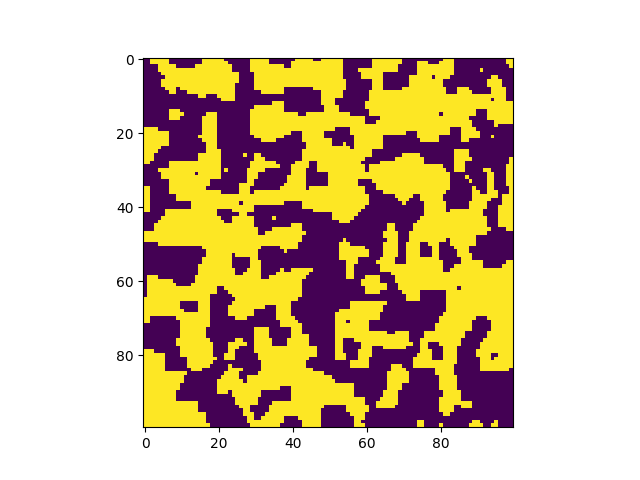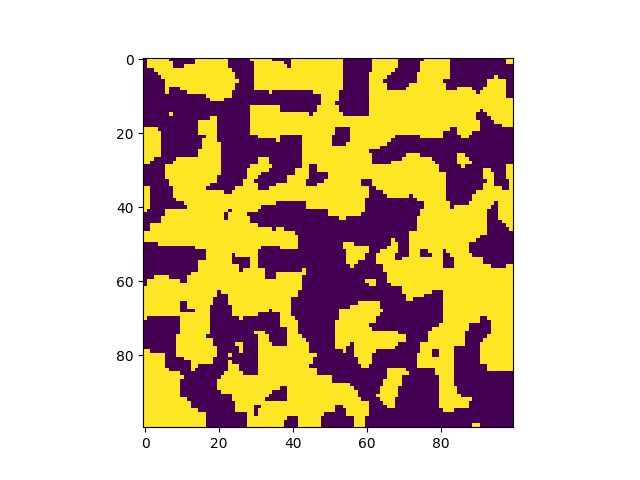
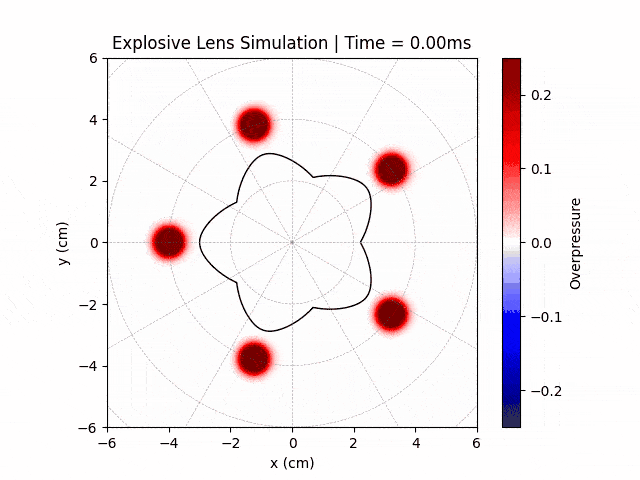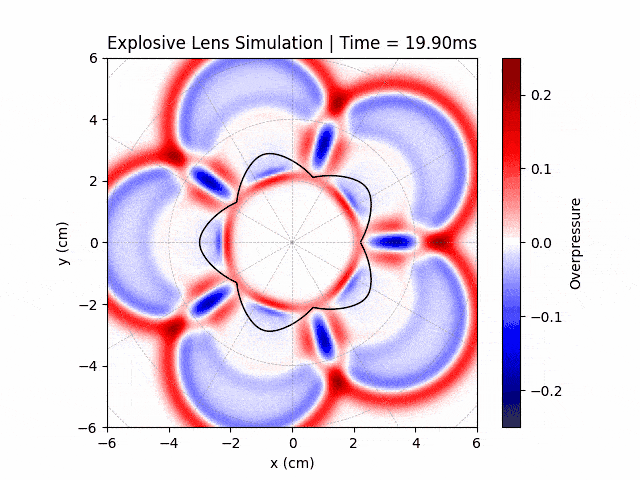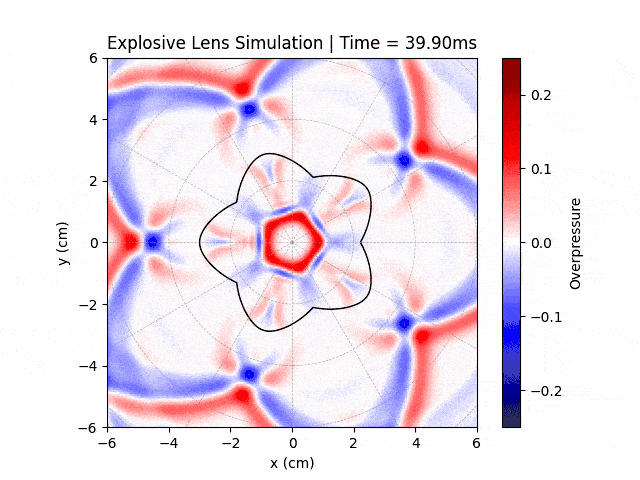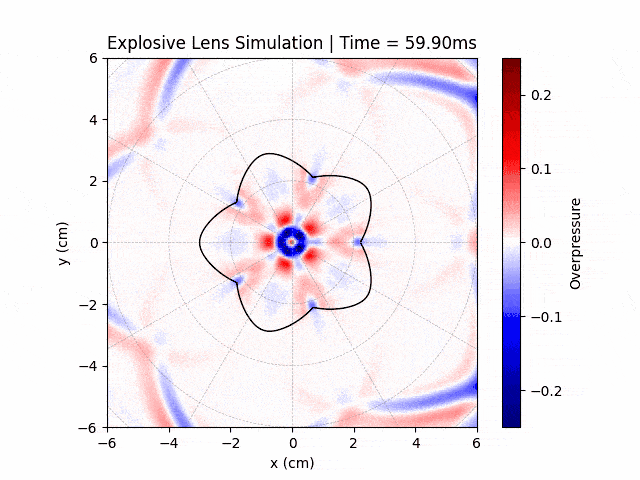
Explosive Lenses
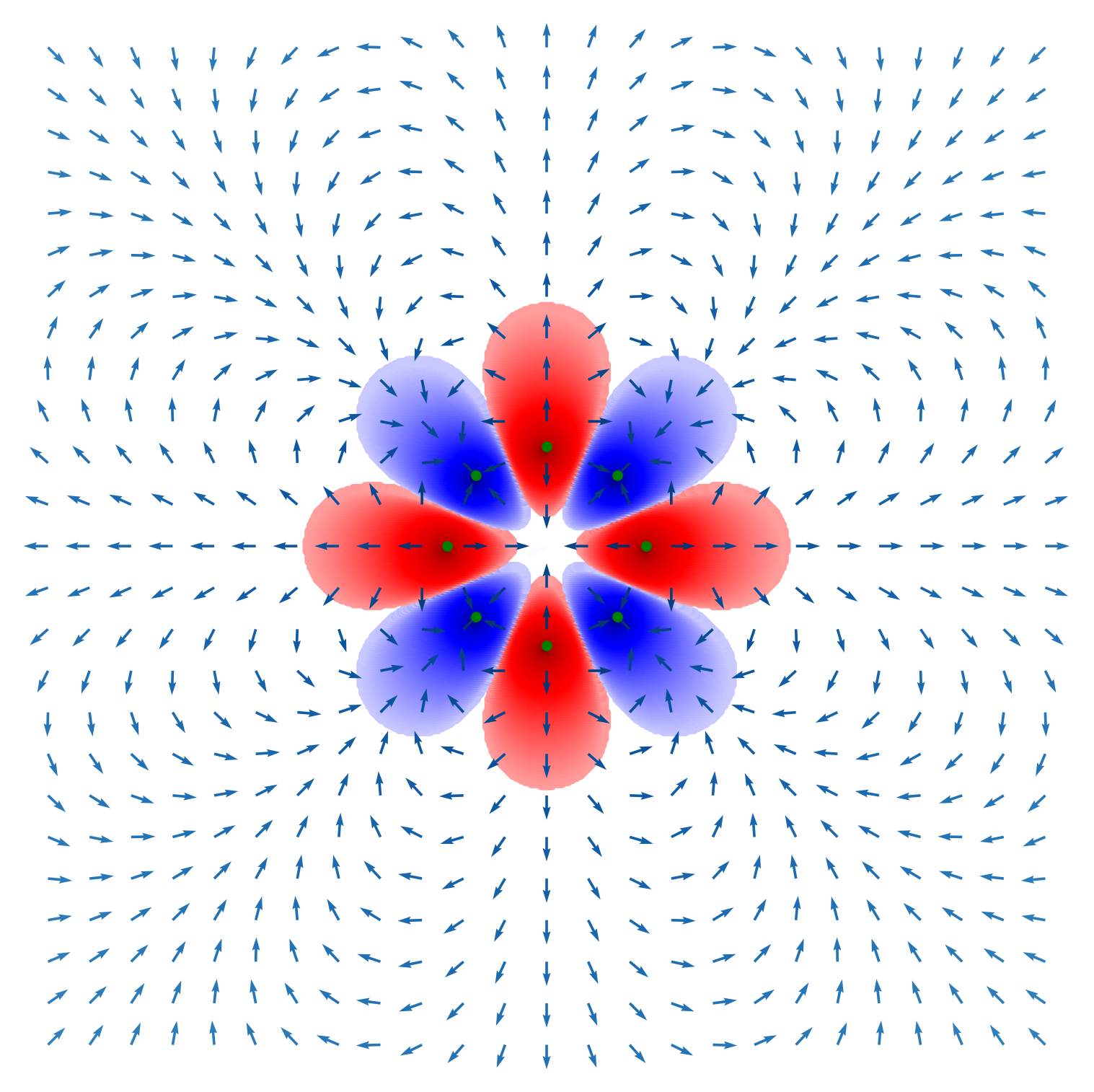
Multipole Field
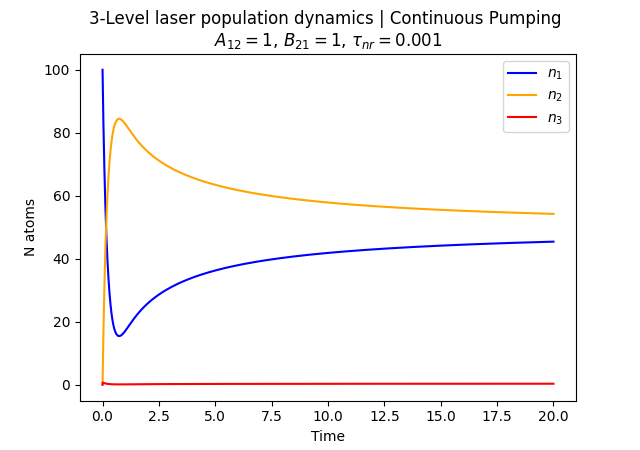
Laser Physics
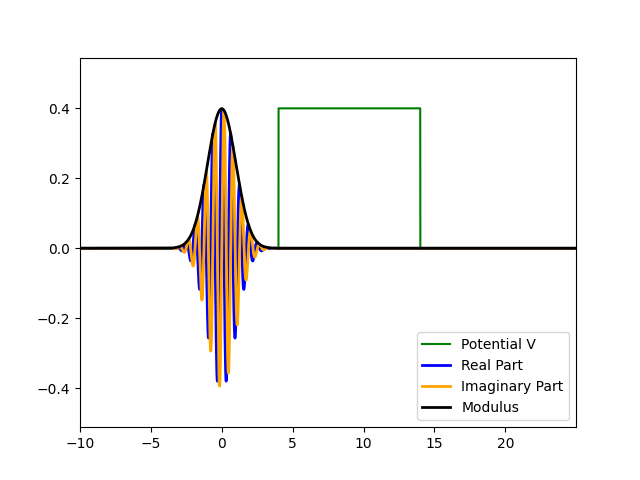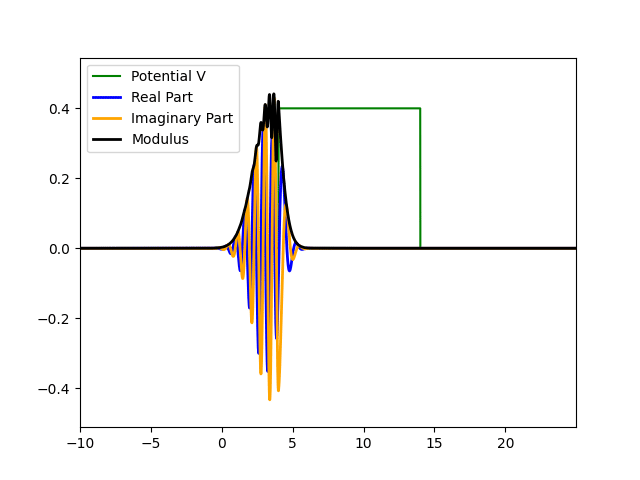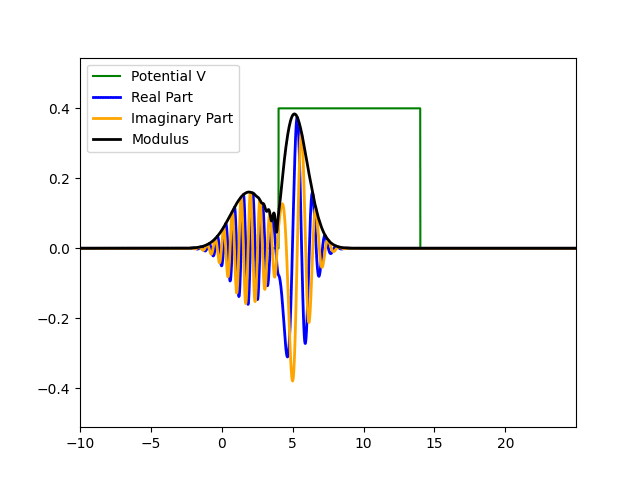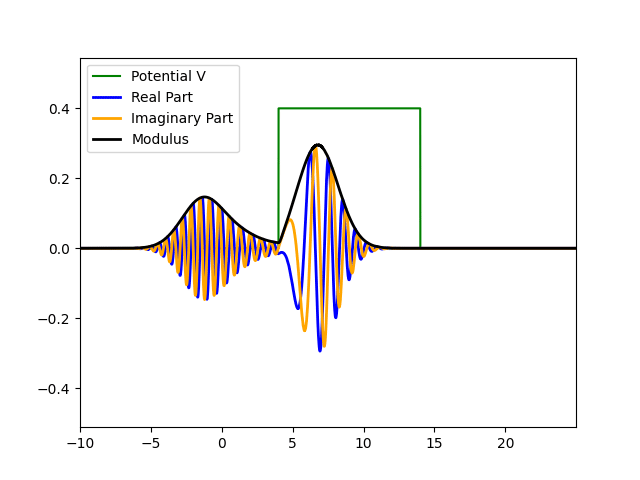
Wavefunction Evolution and Quantum Tunneling
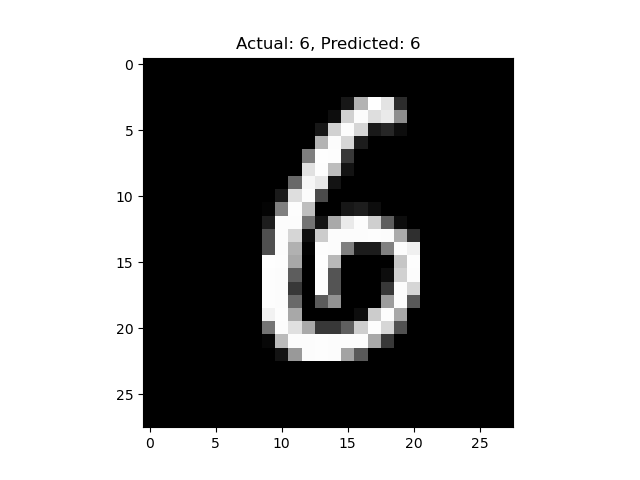
MNIST Character Recognition Neural Network
Electromagnetic Lens and B-field Visualizer
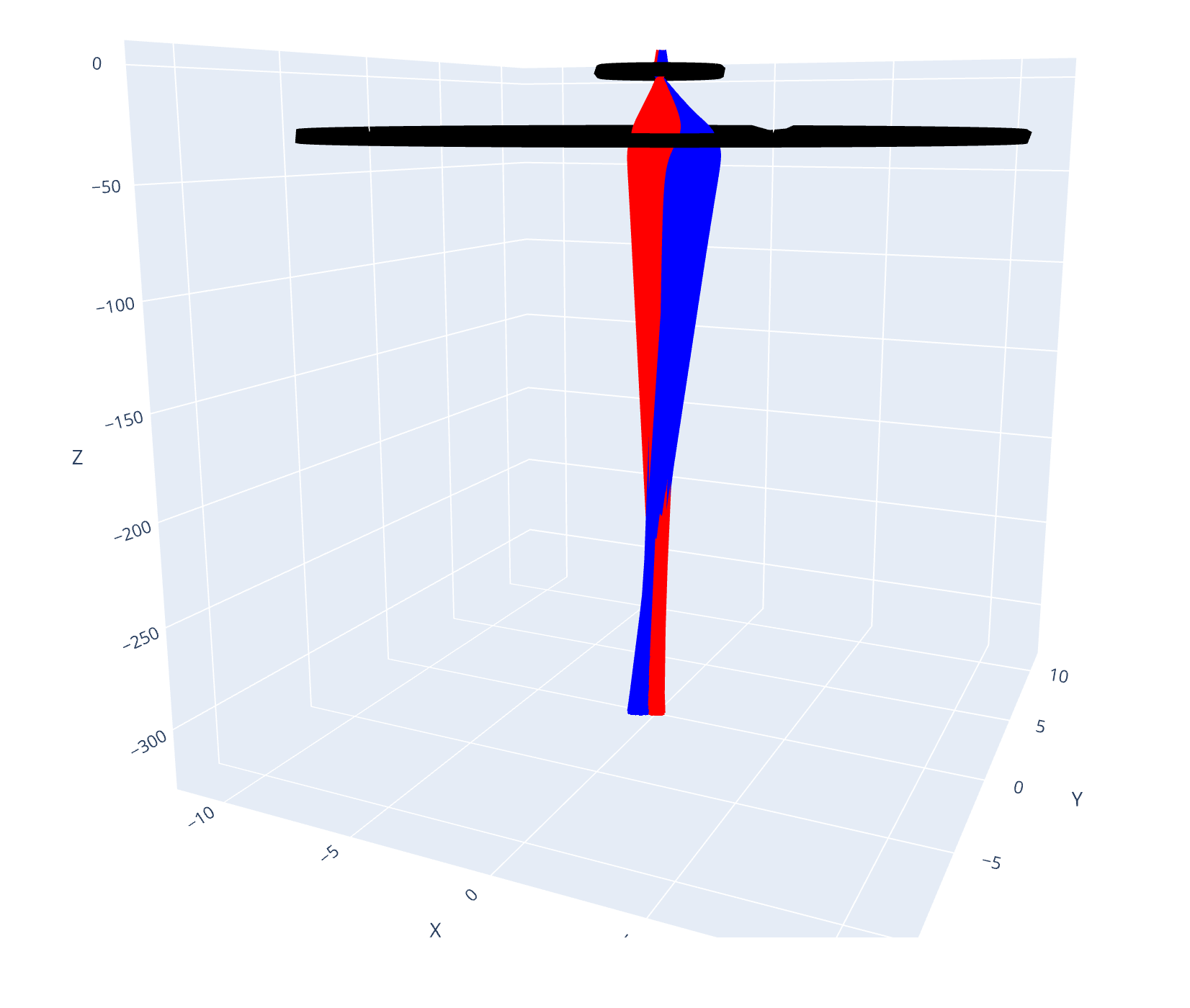
Gravity Simulation
Lennard Jones Crystal
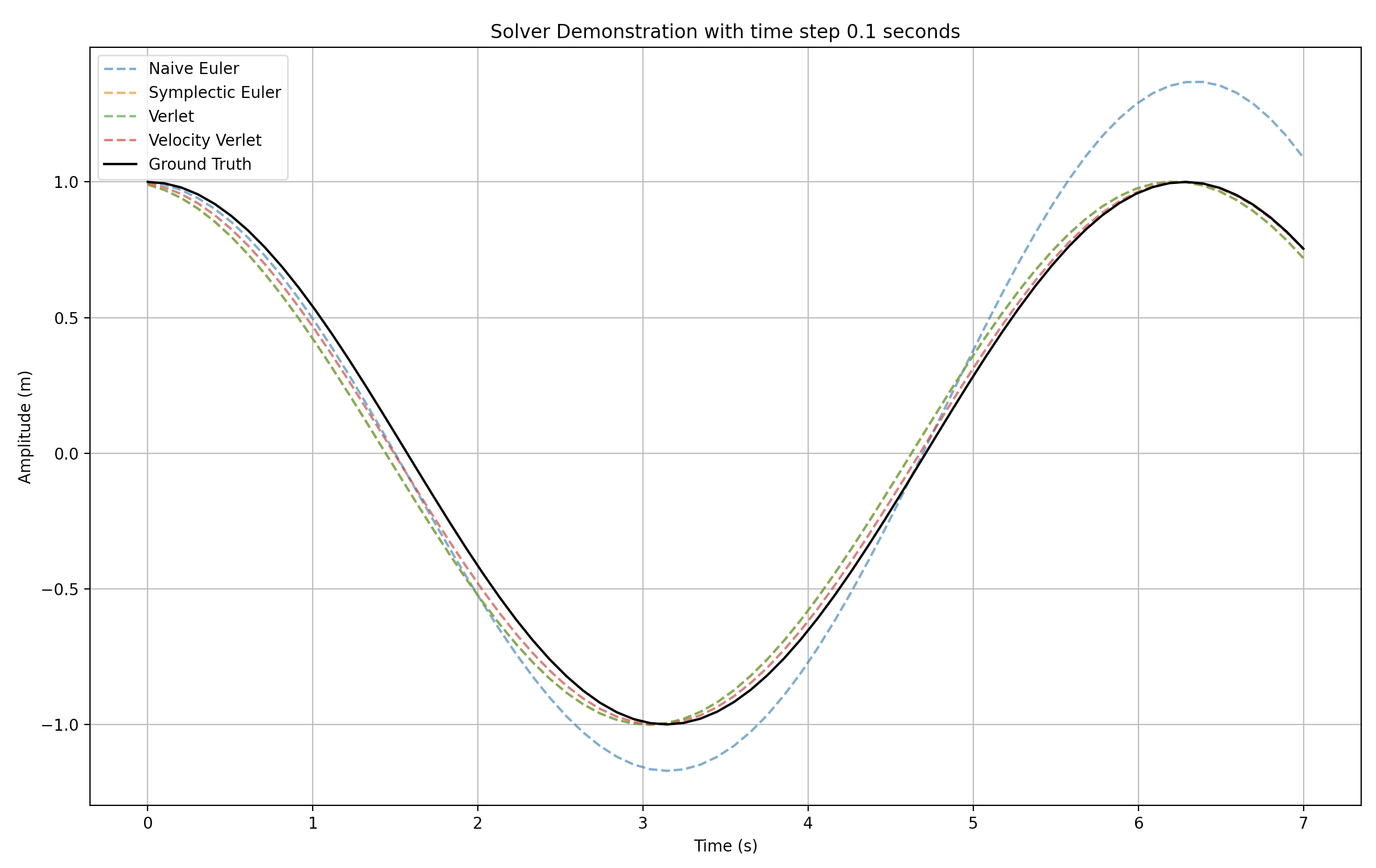
Numerical Solutions Demo
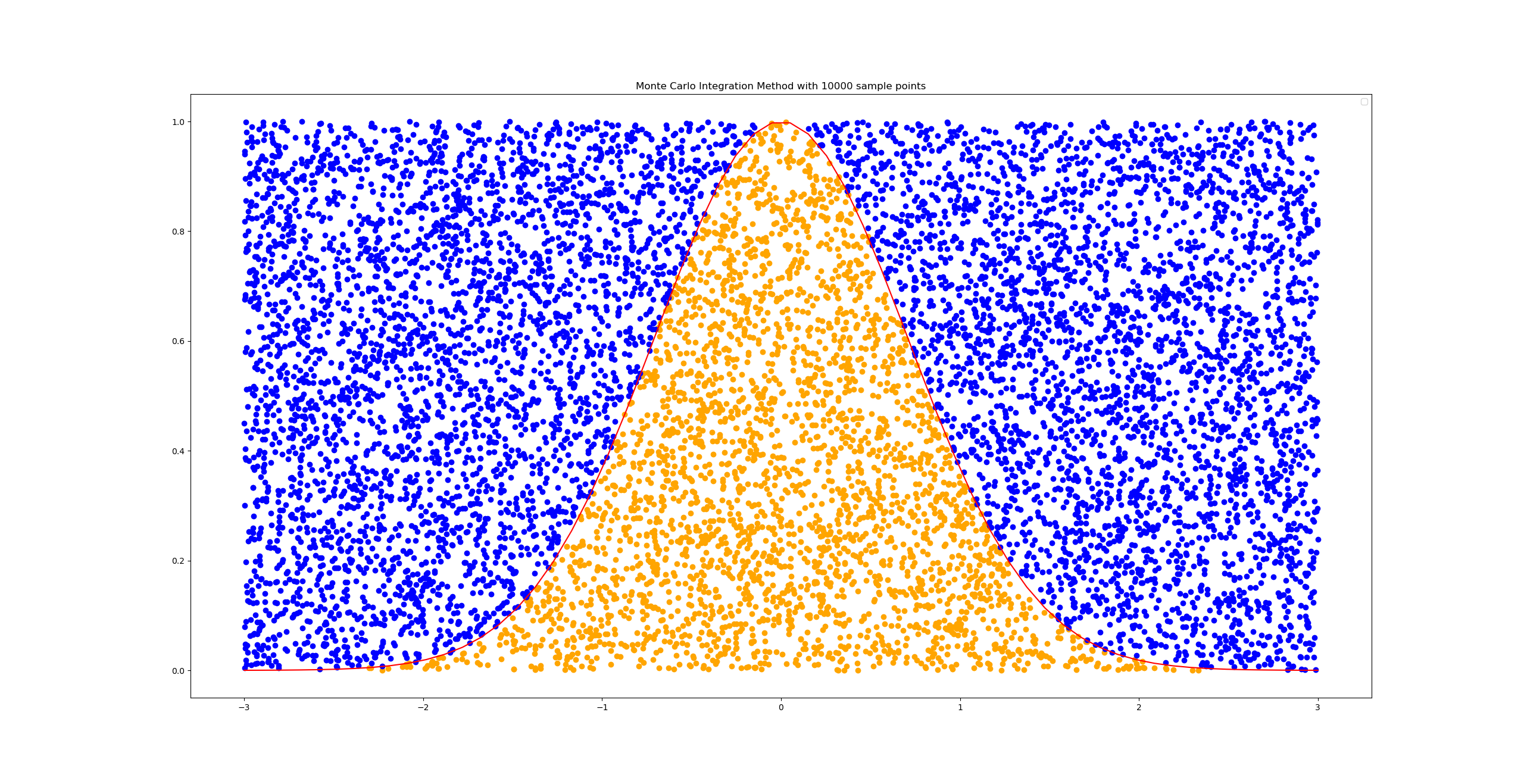
Monte Carlo Integration Demo
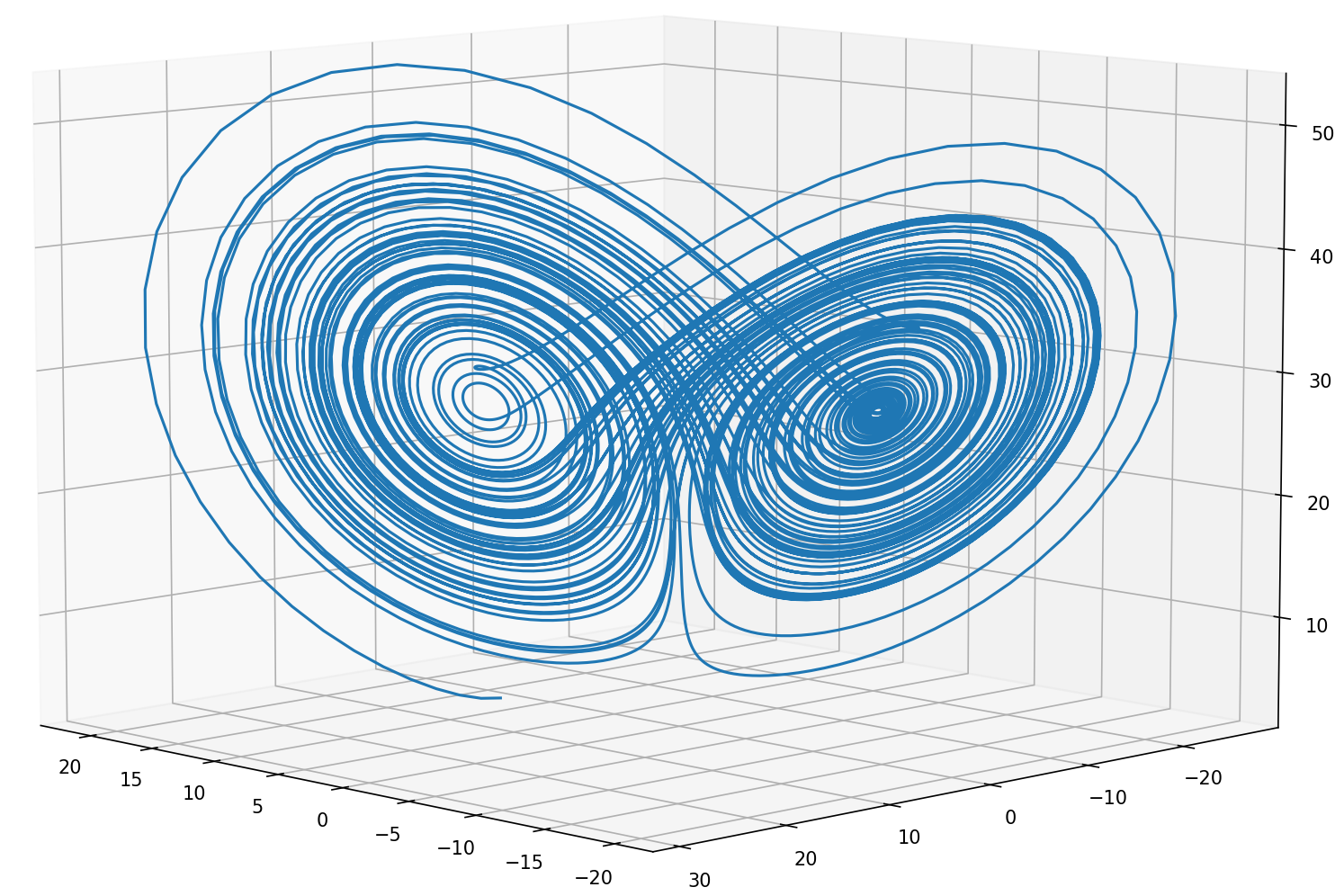
Lorentz Attractor
Einstein Solid
Command Line Video Player
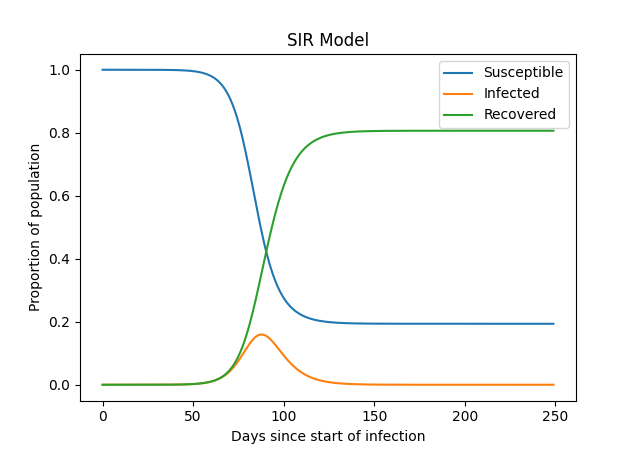
SIR Infectious Disease Model
Black-Scholes Equation and European Options Pricing
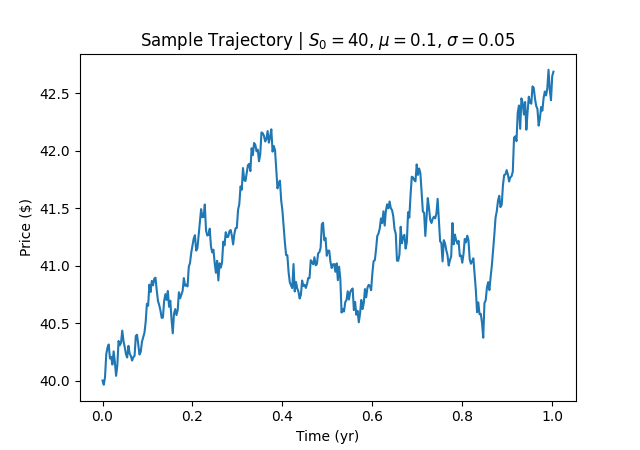
Stock price trajectory
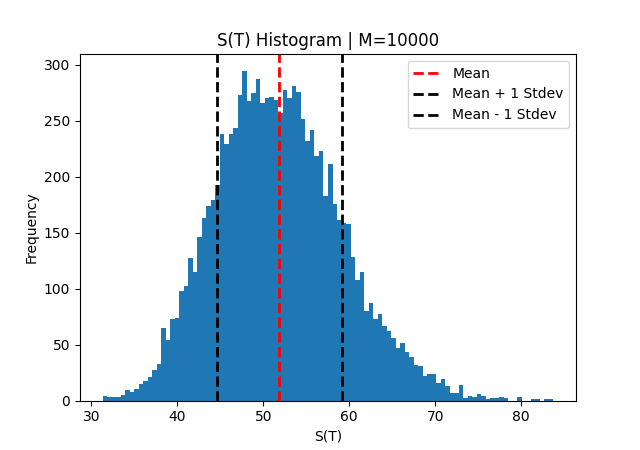
Histogram of future stock prices
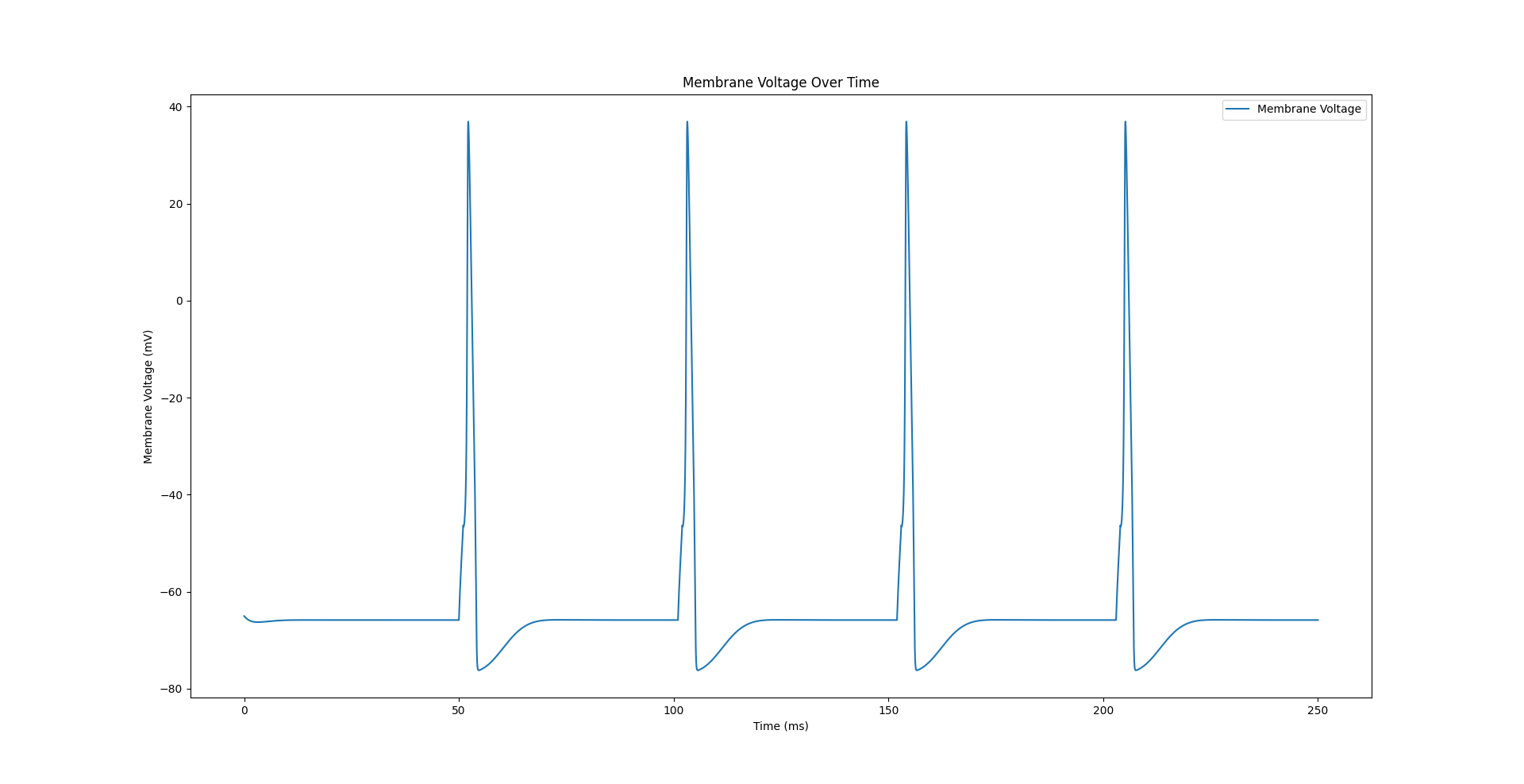
Hodgkin-Huxley Neuronal Dynamics
Projects
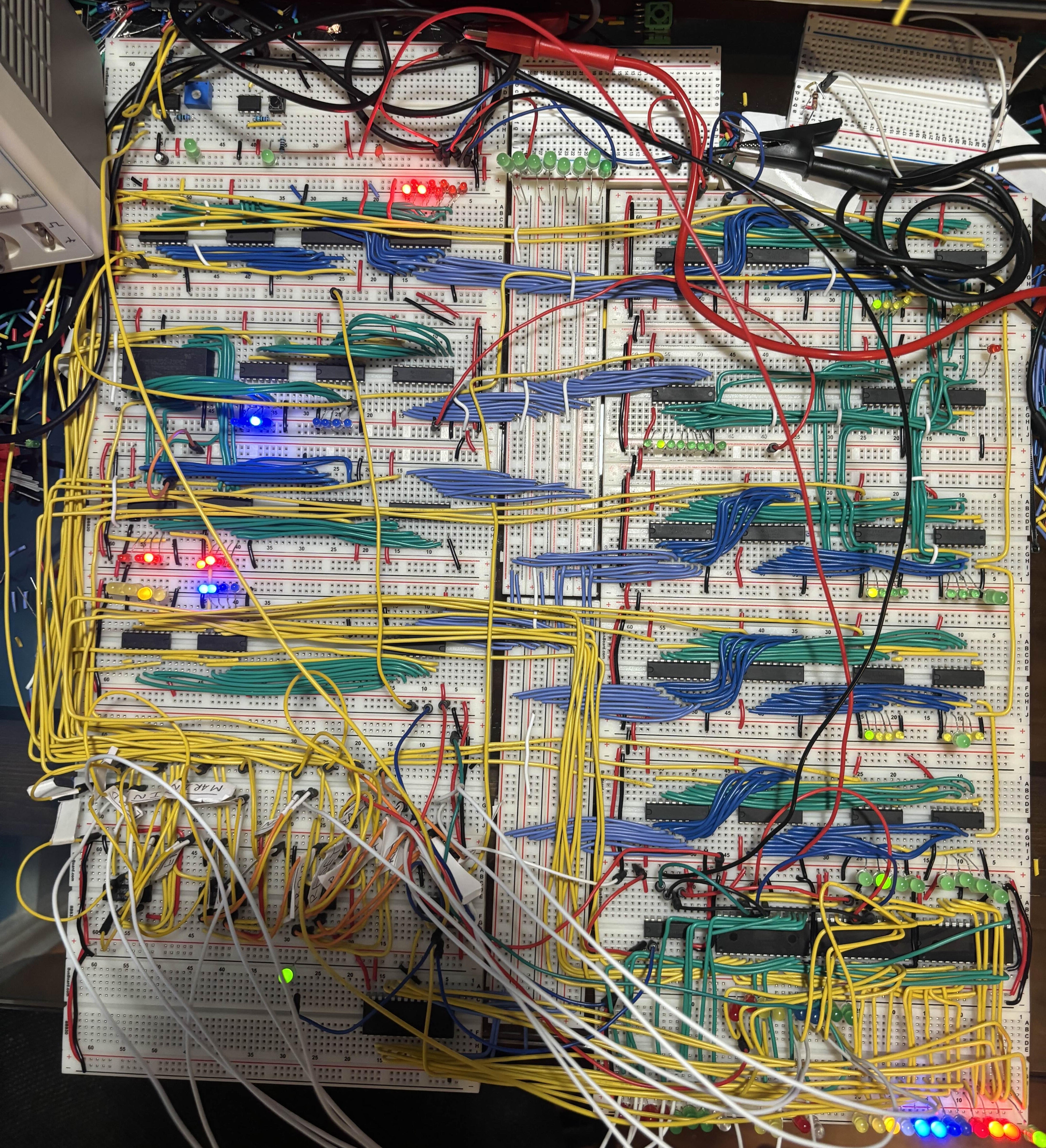
8-Bit Breadboard Computer
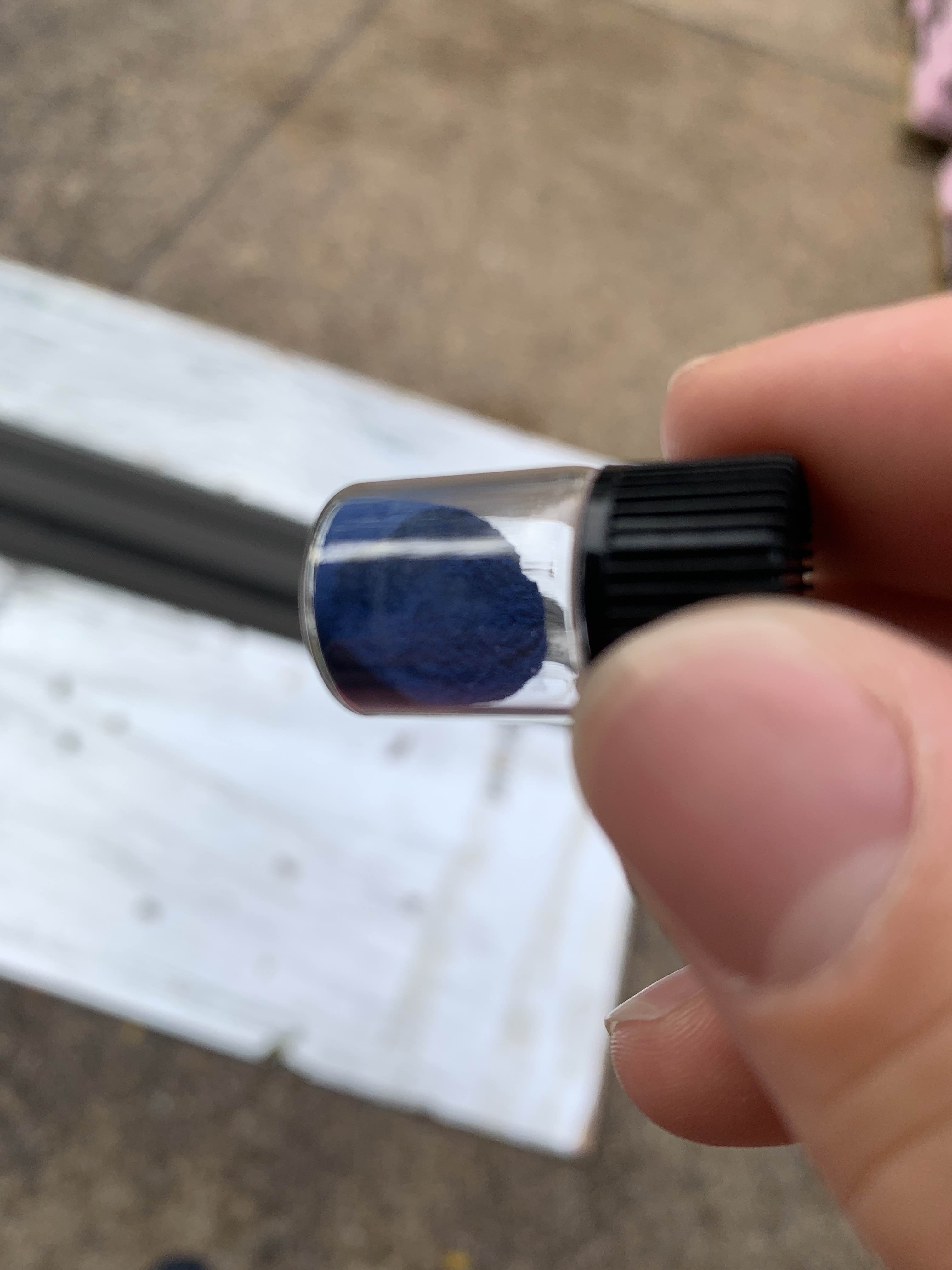
YInMn Blue and Other Pigments
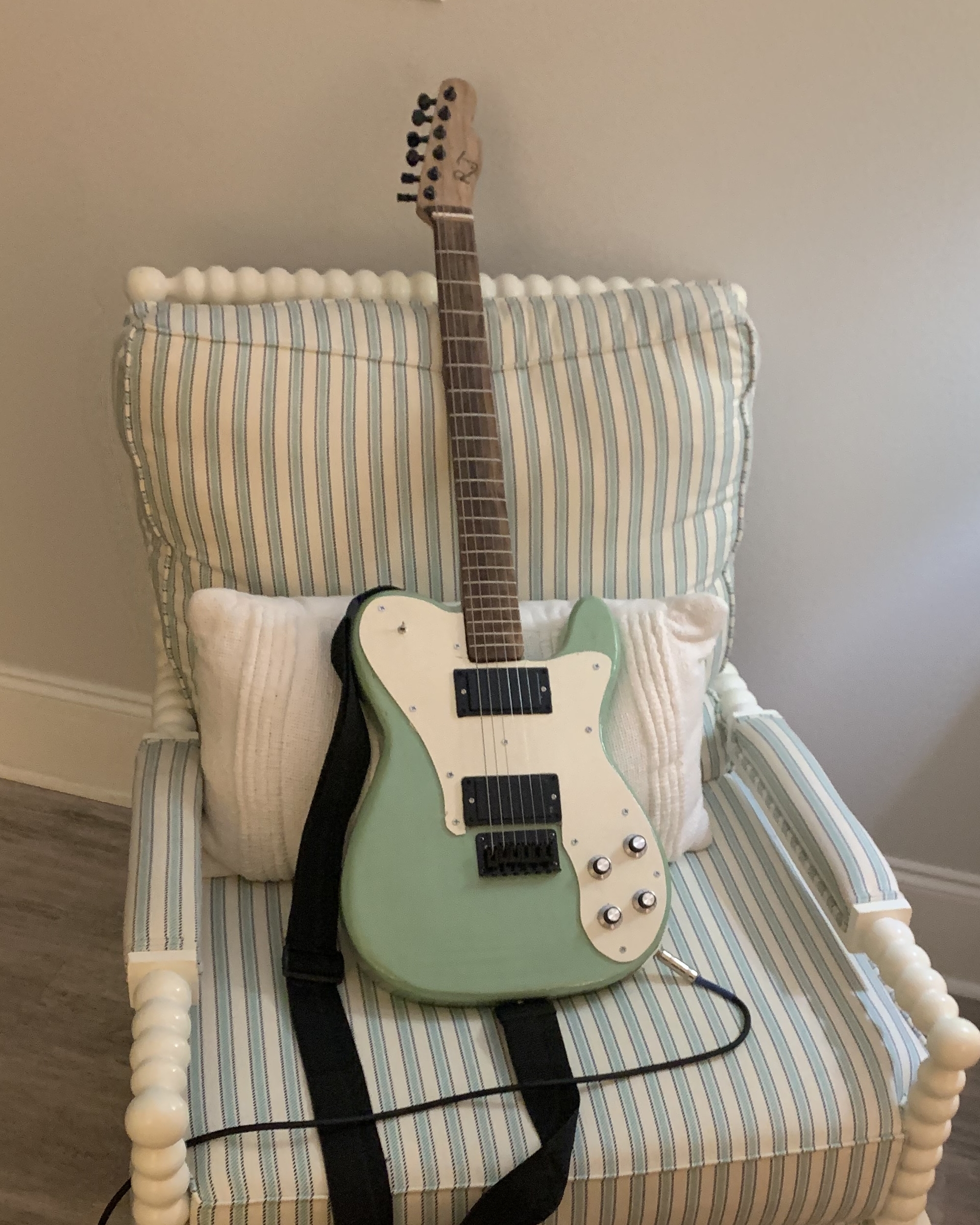
Telecaster Deluxe Electric Guitar


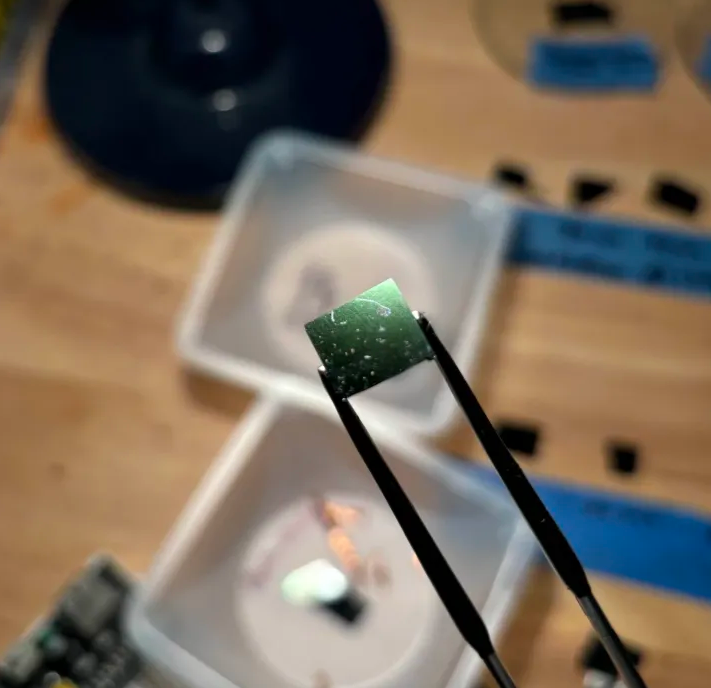
Semiconductors @ Home
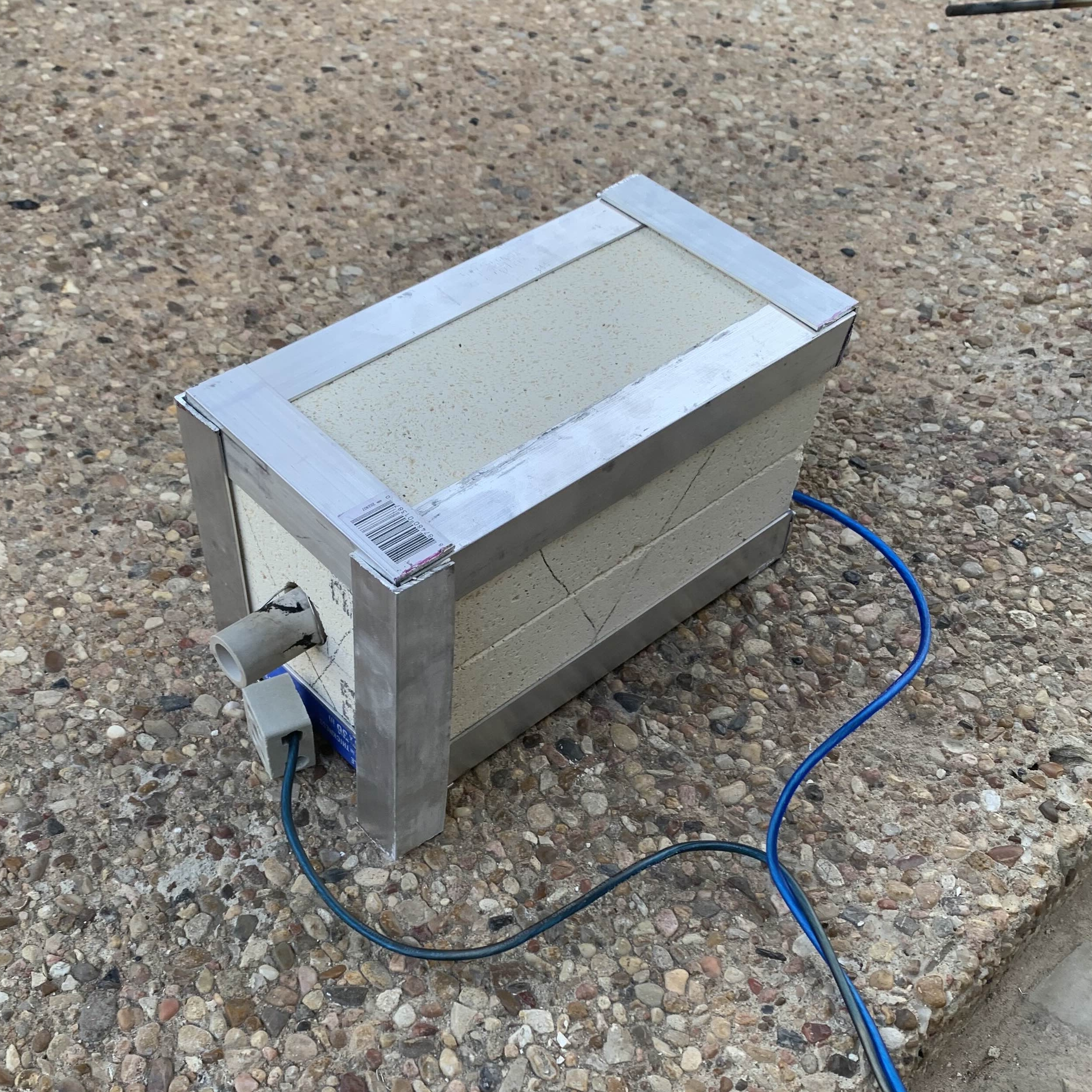
1200°C Tube Furnace


Microwaved Rubies
3D Printed Motor


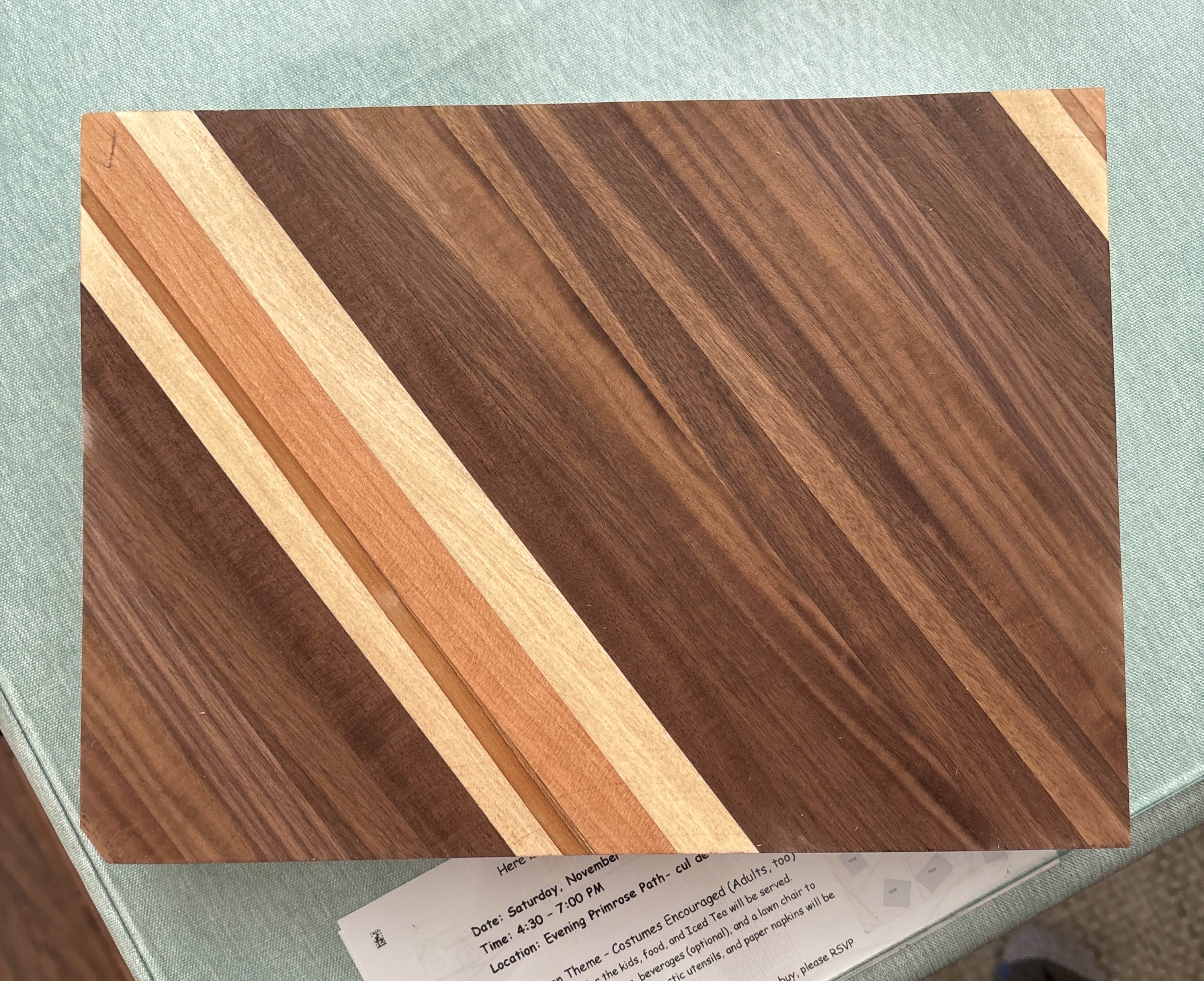
Walnut Cutting Board
Open Source Multielectrode Array (Neuroscience)

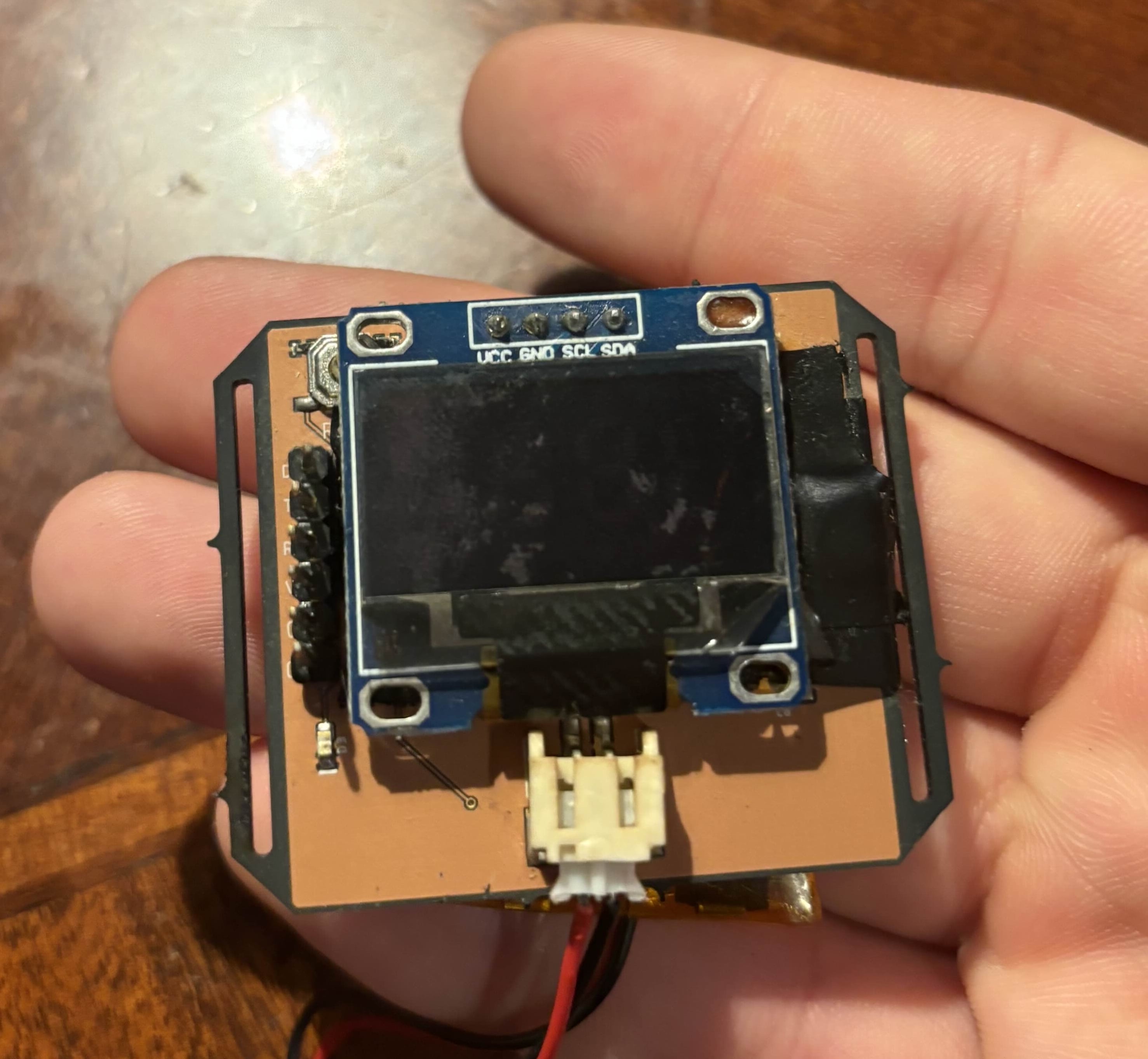
Smartwatch
Educational Resources
Exosky!
This was a project submitted to the 2024 NASA Space Apps Challenge Competition.
ChemHub
This was a project created by me and a friend to help others prepare for chemistry competitions. I wrote the classification algorithm, while the fabulous UI was written by my friend.
Research
Characterization of and Shielding Against Single Event Effects (SEEs) in EEPROMs
Abstract:
This project investigates the vulnerability of EEPROM memory chips to Single Event Effects (SEEs) caused by high-energy particles, replicating cosmic ray conditions using the T9 beamline at CERN. By irradiating memory chips and testing a variety of low-cost shielding materials—including concrete, iron, aluminum, and polyethylene—the experiment aims to quantify and reduce SEE-induced failures. Statistical analysis will determine the effectiveness of each material in mitigating radiation damage. The goal is to inform cost-effective shielding strategies for electronics in space and accelerator environments.
Link to paperExperimental Test for the Role of Short-Range Correlations in the EMC Effect
Abstract:
This is the International Physics Olympiad Cooperation’s 2024 Beam Line for Schools competition proposal. We aim to utilize deep inelastic scattering (DIS) off metal foil targets to test the SRC hypothesis flavor dependence for the EMC effect.
Link to paperElucidating Functional Group Presence by Analyzing IR Spectra with 1-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks
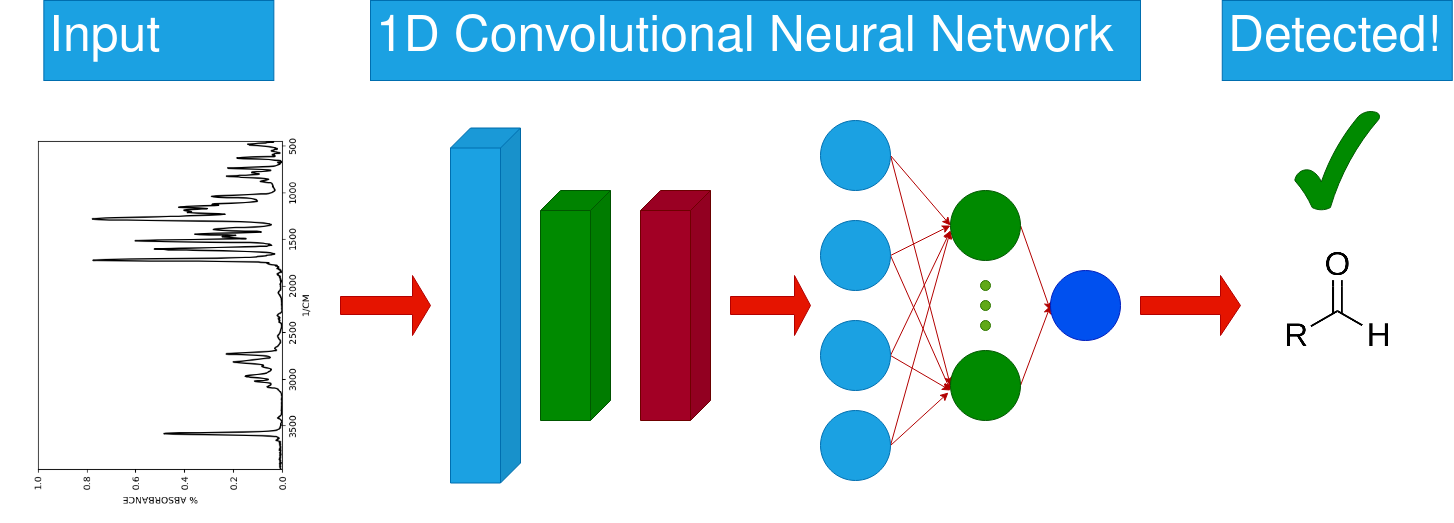
Abstract:
This paper presents a novel solution to the problem of IR spectrum interpretation by applying a 1-dimensional convolutional neural network to classify molecular spectra as either containing a functional group or not containing a functional group. 16 models were trained using a single general model architecture, and 11 were highly effective with accuracy, precision, recall, F1, and AUC scores, all greater than 90%. Phenomenal classification performance was achieved on aldehydes and ketones, where previous attempts have struggled. Furthermore, a tool was developed to generate saliency maps for each model, allowing for the analysis and study of how the model interprets the IR spectra to make classifications. Our results have applications in fields such as the pharmaceutical industry and drug development, as well as the rapid assay screening of environmental pollutants while being generalizable to be a competitive option for any high-volume IR spectroscopy screening process.
Link to paperIn Silico Design of a Novel Cdc14 Phosphatase Inhibitor in Penicillium Digitatum
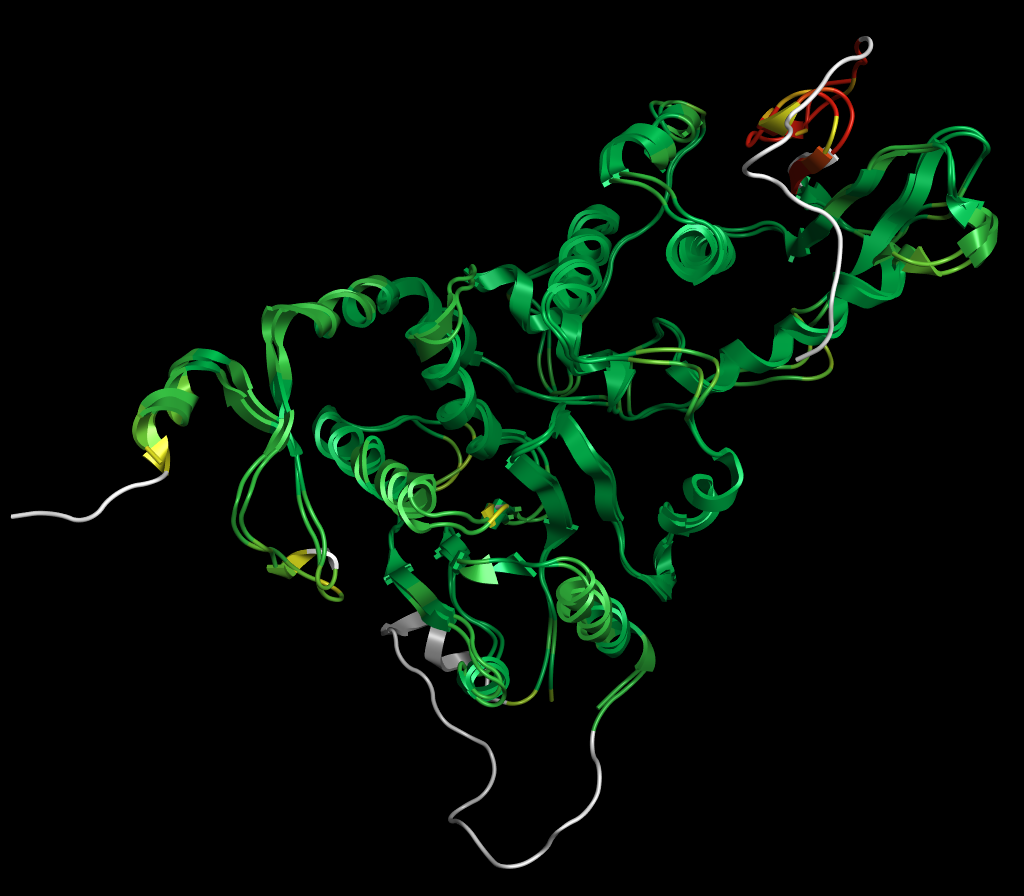
Abstract:
P. digitatum is known for causing a host of economically damaging diseases in citriculture such as citrus green mold disease, wreaking havoc on the global and local markets as a whole. We have developed a novel inhibitor for the Penicillium Digitatum Cdc14 phosphatase homolog (PdCdc14) that is predicted to exhibit broad-spectrum fungicidal properties. Cdc14 is an enzyme belonging to the family of dual specificity protein tyrosine phosphatases, known to play a key role in cell cycle progression within eukaryotes. It exhibits highly conserved activity, structure, and function throughout many fungal species while being absent from land angiosperms, making it an attractive drug target for a broad-spectrum fungicide. Additionally, we have verified a gene predicted to code for a P. digitatum Cdc14 homolog with multiple in vitro activity assays. Three potential inhibitor lead structures were then identified and characterized in vitro.
Paper available upon request